The bats arenāt leaving Burrvilla.
Thatās according to Metro Vancouver, which is overseeing the largest bat colony of its kind in B.C., a 3,000-strong contingent thatās taken up residence in the attic of an historic house in Deas Island Regional Park.
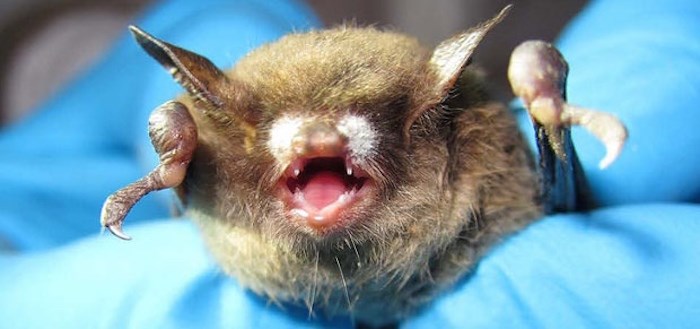 The colony in Burrvilla numbers 3,000, making it the largest in the province. Photo courtesy Metro Vancouver
The colony in Burrvilla numbers 3,000, making it the largest in the province. Photo courtesy Metro Vancouver
āMetro Ā鶹“«Ć½Ó³»has no plans at this time to relocate (or exclude) the maternal bat colony from Burrvilla... The bats peacefully co-exist with the resident caretaker and regular inspections reveal that the bats are respectful guests and do not cause damage to the heritage home,ā a regional district spokesperson explained.
Monitored by the regional district and the South Coast Bat Society, the colony of Yuma bats and brown bats has received a lot of publicity by taking up residence in one of the most historically significant structures still standing in Delta.
In 1906, Harry Burr, whose father supported the incorporation of Delta, built the imposing Victorian-style home on the farm called Burrvilla. The house was a lively social centre for community gatherings, holding teas and weddings in its formal gardens and sponsoring a hunt club. The farm also had its own steamship landing as well as a post office and remained in the Burr family until 1974.
The first house to receive heritage designation from the city in 1982, it was moved from its original location at the corner of River Road and 62B Street to Deas Island for restoration and preservation.
 Metro Ā鶹“«Ć½Ó³»says the bats are respectful guests and arenāt damaging the century-old home. Photo courtesy Metro Vancouver.
Metro Ā鶹“«Ć½Ó³»says the bats are respectful guests and arenāt damaging the century-old home. Photo courtesy Metro Vancouver.
Situated in a regional park on the banks of the Fraser River, the house has now been a home for bats for over 20 years, but only had occasional monitoring until the colony grew and an expanded program was initiated in 2016.
The growth of the colony prompted the City of Delta to raise concerns last year about the state of the century-old house.
āI donāt think thatās what that beautiful house should be used for. I really think they should be creating another space and moving them. Itās a real insult to have that taking place without any thought of removing that experimentation,ā then mayor Lois Jackson told the Optimist following a regional parks committee meeting where her request for another structure to be built for the bats was denied.
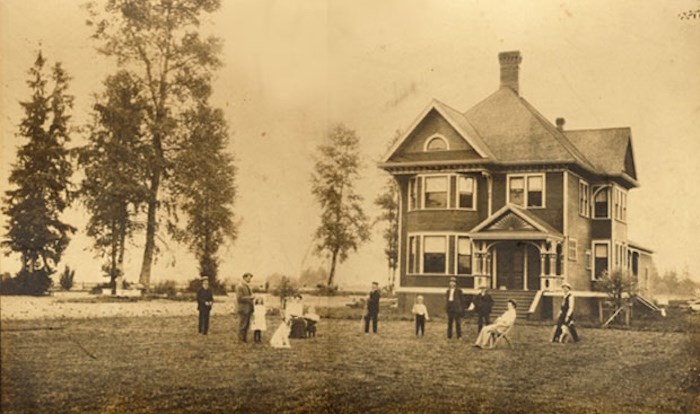 The home in early 1900s, reflecting the turn of the 19th Century economic expansion of Deltaās farming industry, and symbolizing the wealth and status attained by the prominent Burr family. Delta Archives
The home in early 1900s, reflecting the turn of the 19th Century economic expansion of Deltaās farming industry, and symbolizing the wealth and status attained by the prominent Burr family. Delta Archives
Delta council asked the regional district to provide a report on the bat colonyās impact on the structure, including the effectiveness of measures being used to protect the building, as well as best practices used in other jurisdictions for the protection of historic buildings that are home to bats. The city also asked for clarification on the issues relating to the potential relocation of the colony.
Since then, city officials have had a site visit, including to the attic, and have found that the regional district appears to be doing a good job managing the batsā impact on the house, Mike Brotherston, Deltaās manager of climate action and environment, recently told the Optimist. He said theyāll be doing some follow-up visits.
In a letter to Delta council, Tom Bearrs, president of the Delta Naturalists Society, warned that moving the important colony would be difficult for several reasons.
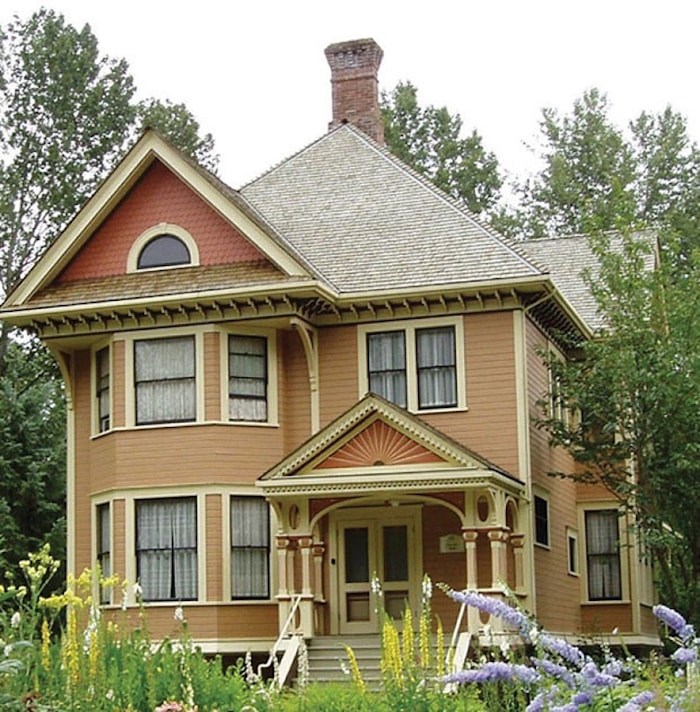 Burrvilla was moved to nearby Deas Island Regional Park in 1982. Optimist file photo.
Burrvilla was moved to nearby Deas Island Regional Park in 1982. Optimist file photo.
āWith such a large colony, it would require at least two large ābat condosā in the area to house them. Building and installing these would be a monumental undertaking. And there is no certainty that these bats would accept an alternate artificial new roost. The impact on trying to move these sensitive animals would more than likely be tragic,ā Bearrs stated.
Alan Burger, president of B.C. Nature, wrote how bats in their nightly forages consume huge numbers of insects, including mosquitoes. A lactating female can eat up to 1,000 insects per night, he explained. āThe benefits to the community are numerous. In fact, you might say that bats perform a valuable public service.
āMetro Ā鶹“«Ć½Ó³»staff clean the attic of guano (bat droppings) when the bats are not in residence. These staff are conscientious with regard to the condition of Burrvilla and state categorically that the droppings are not harming the house.ā
Little brown bats are listed as an endangered species due to the threat of white-nose syndrome, a disease caused by an invasive and highly infectious fungus, which has added more importance to monitoring the colony.
Last fall at Deas Island Regional Park, the province announced that $40,000 would be directed to help combat white-nose syndrome. The pathogen first turned up in North America in 2006 and reportedly by 2012 was associated with at least five to seven million bat deaths.
The Metro Ā鶹“«Ć½Ó³»parks committee received an update last year on the monitoring of the colony at Burrvilla, which included a capture-mark-recapture pilot study, which didnāt detect any signs of white-nose syndrome.
A report to the committee also noted that in 2016, acoustic monitors and ultrasonic microphones were set up to study bat foraging within the park, which found that six different species use the park and surrounding area as habitat, including the Mexican free-tailed bat, a new species emerging in B.C.
āThis data indicates Deas Island Regional Park is part of a broader habitat network that supports regional bat diversity,ā the report states.


